What is Drone Mapping
Drone mapping is using a camera equipped fixed wing or rotary wing drone also known as a UAV or UAS in conjunction with an autonomous flight controller application on a tablet, smartphone or laptop to acquire data via a sequence of images using a predetermined flight path. The image sequence then being processed using photogrammetry software to create a data type called a point cloud.
Today, the low price point of small UAV drones in combination with advanced photogrammetry software that employ Structure from Motion techniques have lead to as increased interest in image based terrain mapping.
Drone Mapping in industry today
Drone mapping is changing the way aerial data is captured, analysed and distributed and is benefiting many industries across the globe including:
- Agriculture – crop health monitoring, weed analysis, biomass/yield estimation
- Surveying – terrain analysis, erosion assessment
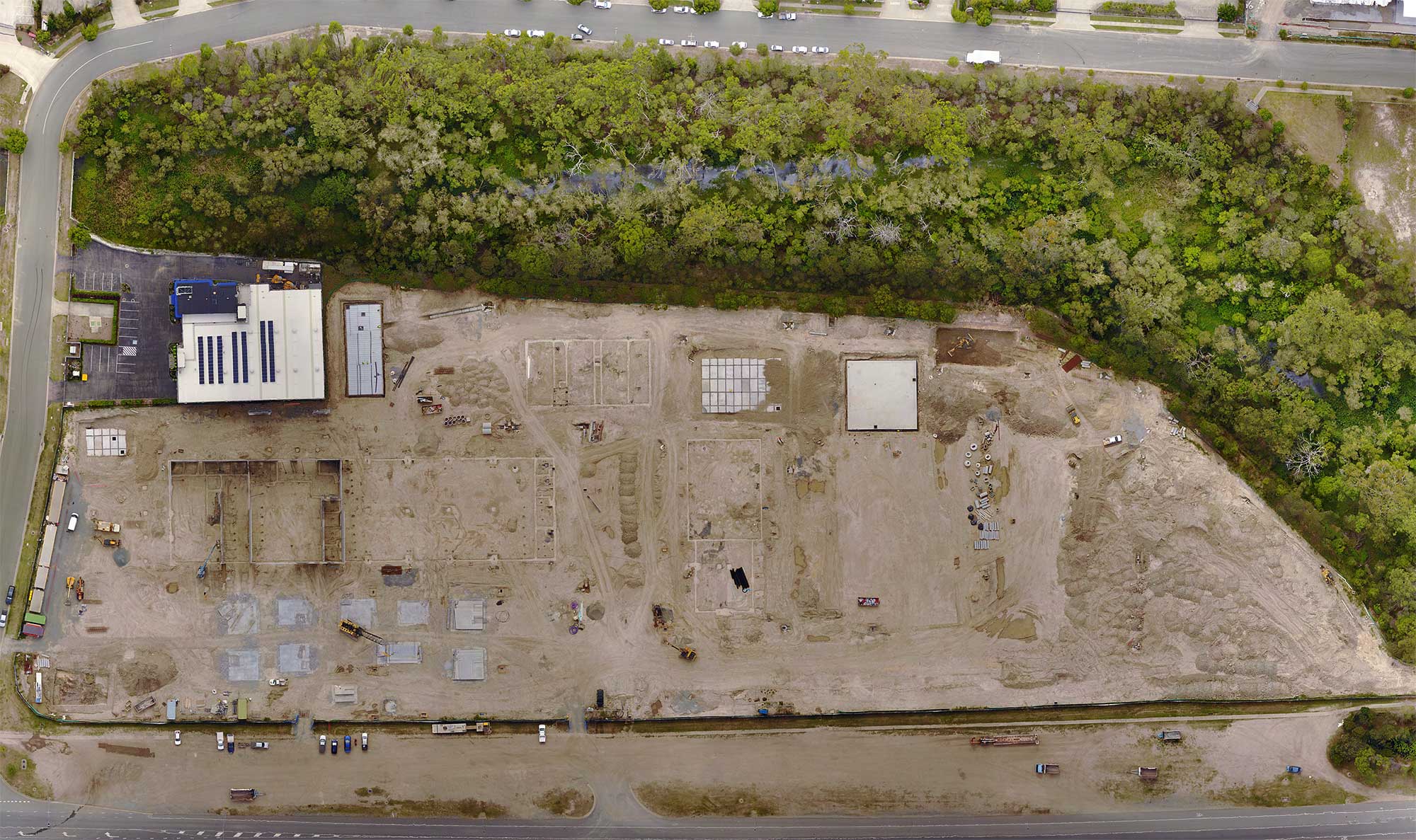
- Construction – compare design plans to as-built
- Mining and quarries – stock pile estimation
Drone Mapping Key Components
The key components to any drone mapping platform are:
- GPS enable drone (DGPS or RTK for accurate survey work)
- High resolution camera
- Autonomous flight control app
- Photogrammetry software
While GPS enable drones are able to capture georeferenced images for use in photogrammetry software to make maps, for any accurate survey grade data including orthomosaics, Differential GPS, Ground Control Points (GCP) or Real Time Kinematics (RTK) need to be incorporated into the capture work flow.
If LIDAR is used in drone mapping platform to acquire data instead of a true color camera , then photogrammetry software is not required as LIDAR captures its data as a point cloud. This saves considerable time, however LIDAR is still a relatively expensive data acquisition technique.
GPS Enable Drone
Today’s drones are relatively small, lightweight, portable, easy to fly and fast to deploy. Equipped with high resolution cameras, they are the ideal low cost mapping platform. There are a large selection of free or affordable apps on the market for IOS and Android devices that extend the usage of drone and assist a drone pilot, the main ones for drone mapping are the autonomous flight control apps, one of the key ingredients in drone mapping.
Benefits of using drones as mapping platforms:
- Fast to deploy
- Easily redeployable
- Minimal disruption to surrounds
- Low environmental impact with much smaller carbon footprint compared to manned flight & manned vehicles
- Can operate under cloud cover
- Safer than manned flight


High Resolution Drone Cameras
High resolution cameras found in modern day drones combined with their ability to fly at the relatively low altitudes (50-75m AGL) provide for highly detailed and accurate maps.
The ground sampling distance (GSD) represents the camera’s ability to resolve detail on the ground and is a function of the following parameters:
- Camera sensor size
- Camera resolution
- Camera focal length
- Drone flight height above the terrain
The GSD can be seen as the real-world size of a pixel if projected from the camera down onto the ground. A GSD of 3 cm/pixel means the map or model generated from the photogrammetry process will be accurate down to 3cm
A larger GSD indicates an image with lower spatial resolution and less visible detail.
Autonomous Flight Control Apps
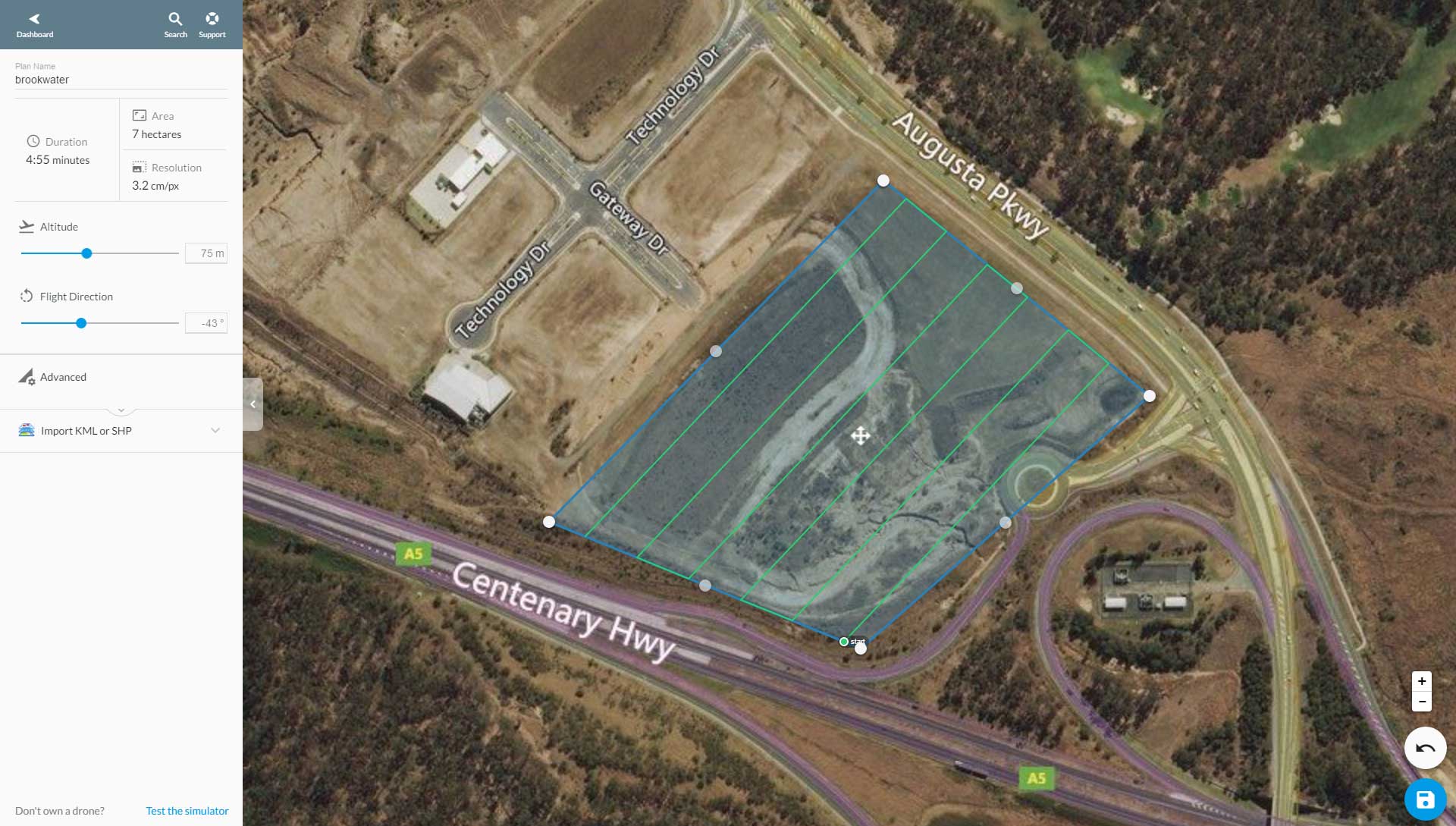
The ultimate success of any drone mapping mission depends on good quality photography and therefore good flight planning is critical. Autonomous flight control app software have intuitive interfaces, where the operator chooses a parameter representing the area of interest to be mapped and the software will fill the area with a predetermined circular or lawnmower pattern flight path.The operator can change the overlap, sidelap and height parameters and get feedback in real time as to how the GSD will be affected.
At DroneAce, we currently use DroneDeploy for all our autonomous drone mapping missions as it interfaces seamlessly with the DJI MavicPro and DJI Phantom 4 Pro as well as providing a platform for processing the captured photography data sets on the cloud if necessary.
Photogrammetry Software
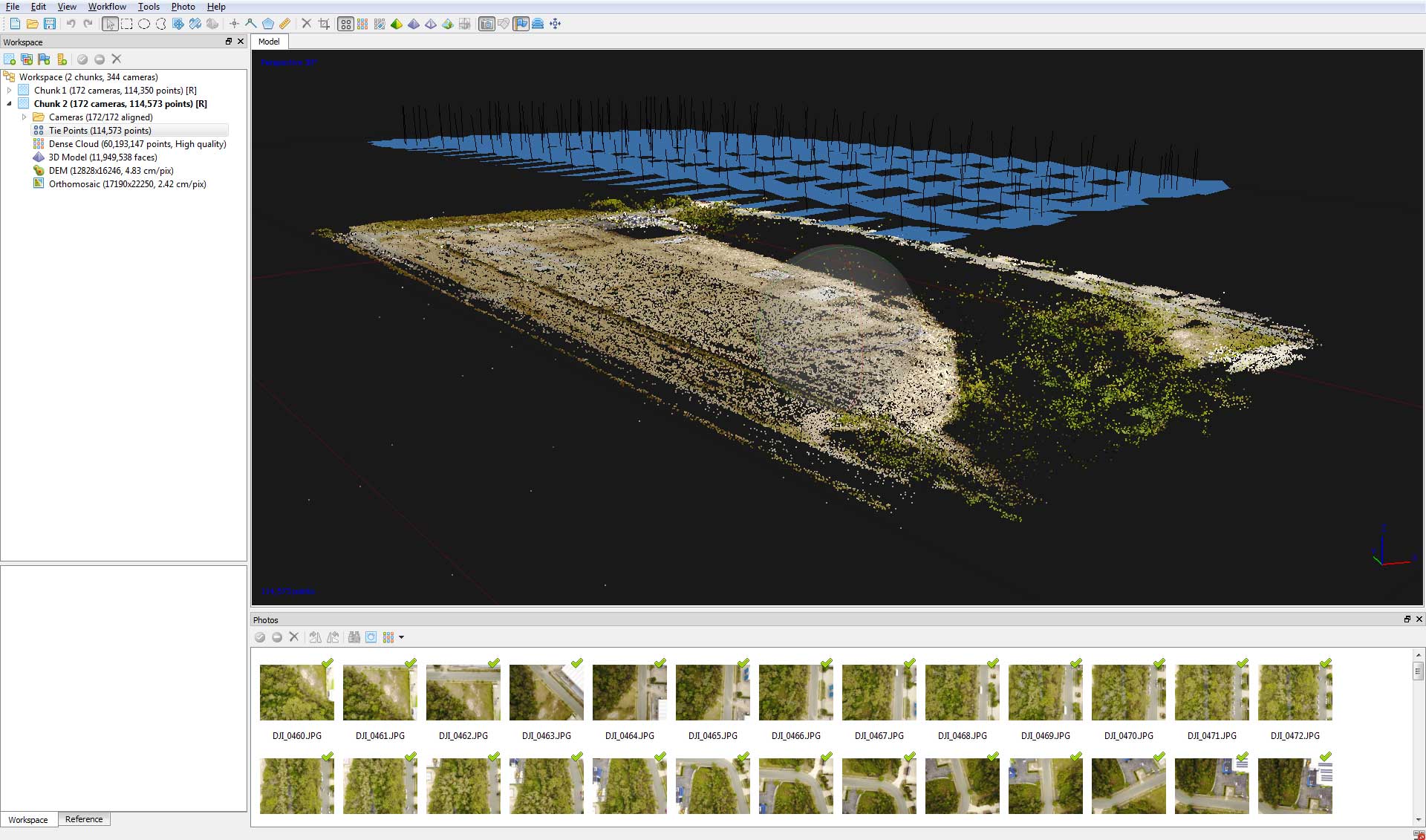
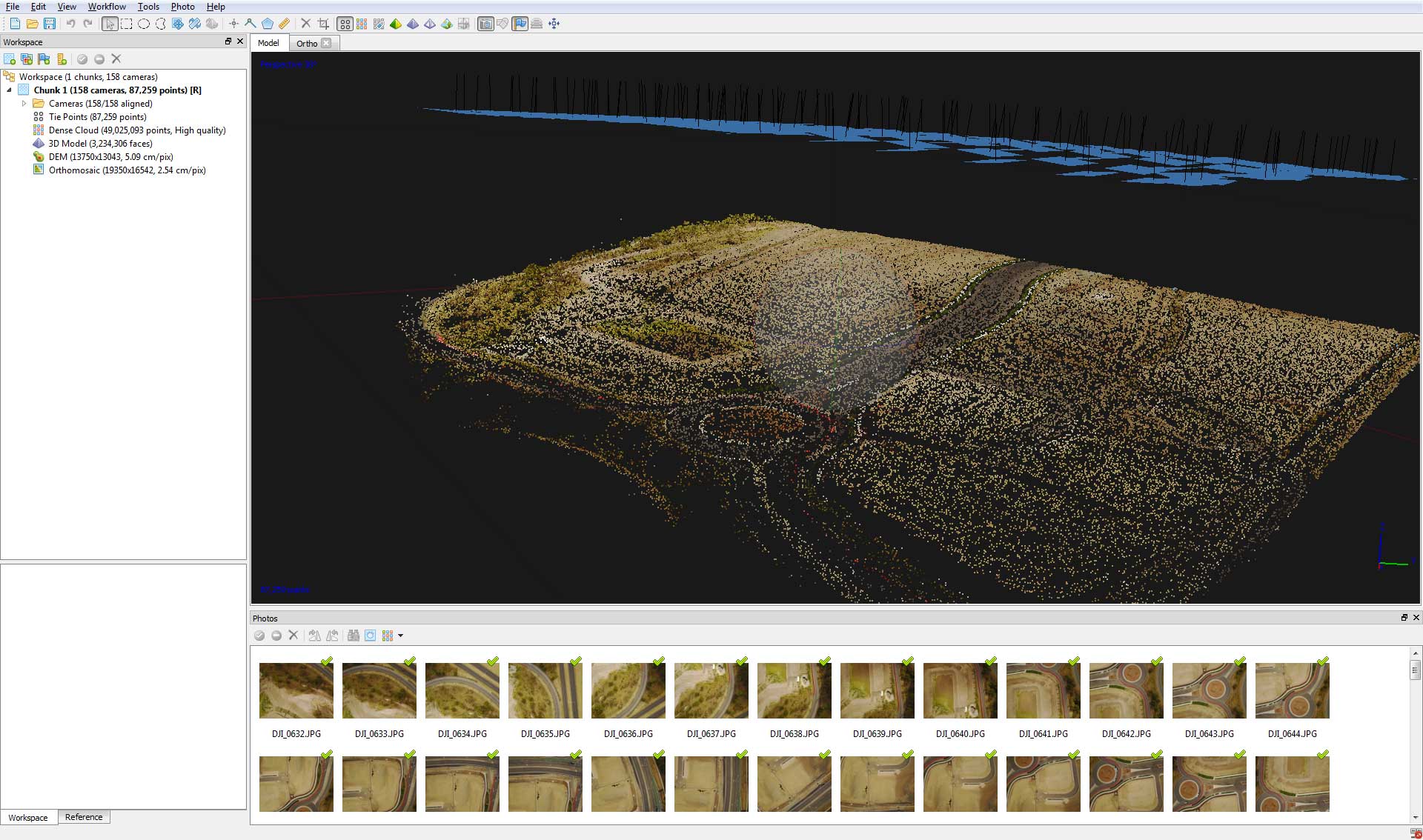
Photogrammetry is the process of taking measurements from photographs. Today’s modern photogrammetry programs like Agisoft Photoscan and Pix4D use techniques including machine vision, pattern recognition and Structure from Motion (SfM) algorithms to turn a serial of images into 3D structures.
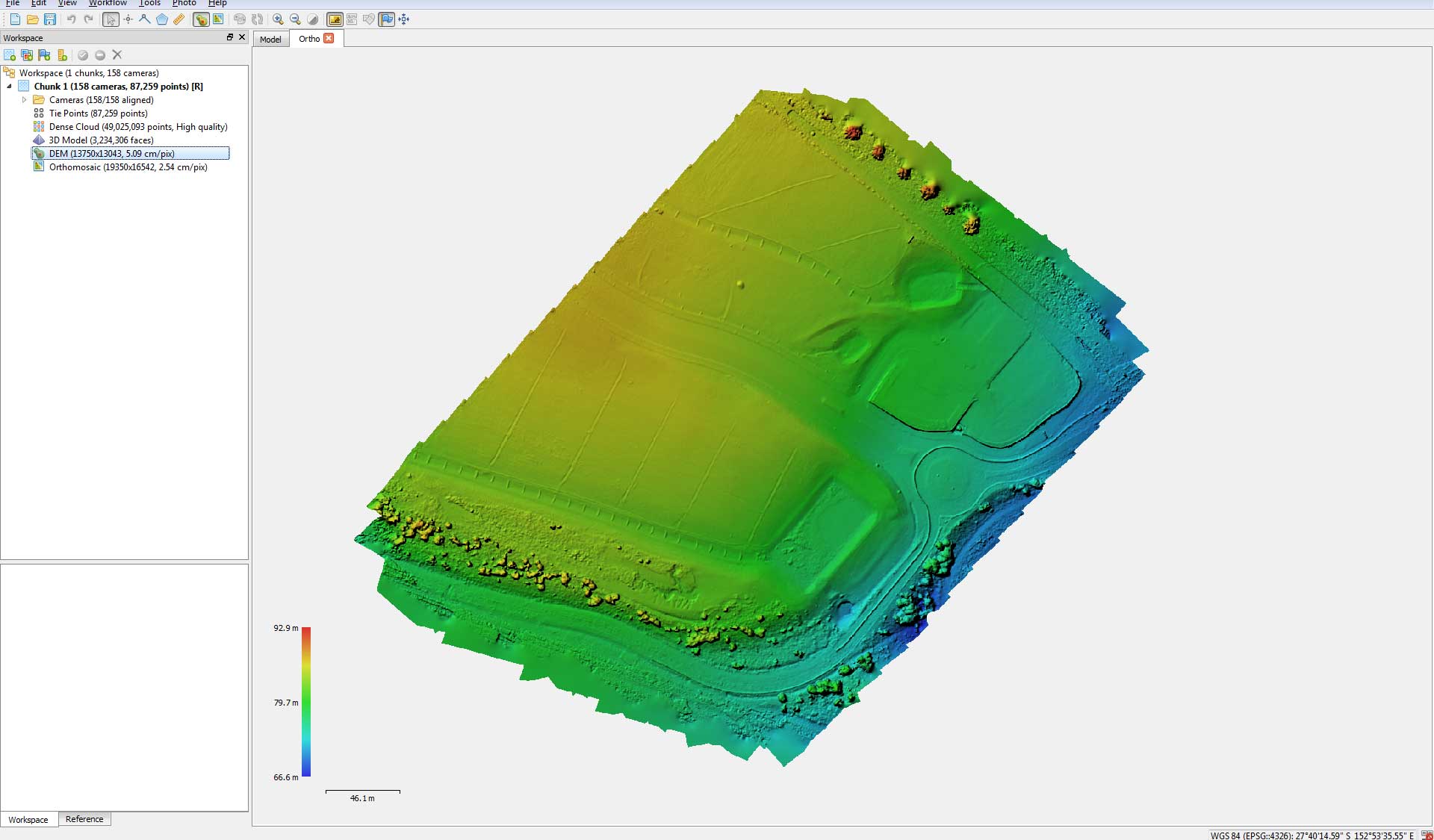
The initial output of the photogrammetry process is a point cloud, a data type which is then used to generate Digital Terrain Models (DTM), orthomosaics or even a 3D mesh. Point clouds and orthomosaics are often using in Graphic Information System (GIS) software programs such as Google Earth Pro or ArcGIS for further analysis.
Depending of the data set (number of images and the image resolution) and processing computer specifications, the photogrammetry process can take many hours or even days. Some programs such as Bently Context Capture and Agisoft Photoscan allow for grid computing where the complex mathematical calculations are distributed amongst a cluster of computer that work in parallel to reduce the processing time considerably.
Using GPU equipped computers will speeds up the photogrammetry process as certain steps involved in the complex calculations (generation of the dense point cloud) are able to use the GPU instruction sets.
While photogrammetry programs represent a considerable investment in the drone mapping pipeline, both in monetary terms as well as the time taken to master, there are alternatives out there and they are found in the Cloud.
Drone Mapping and The Cloud
Cloud based drone mapping service providers such as DroneDeploy and MapsMadeEasy offer a viable alternative to desktop based photogrammetry software. Using grid computing, they offer affordable, tiered pricing the possible only downside is the lack of user input and the considerable time involved in moving the data to the cloud especially in regional or even remote parts of the world with less than adequate upload speeds.
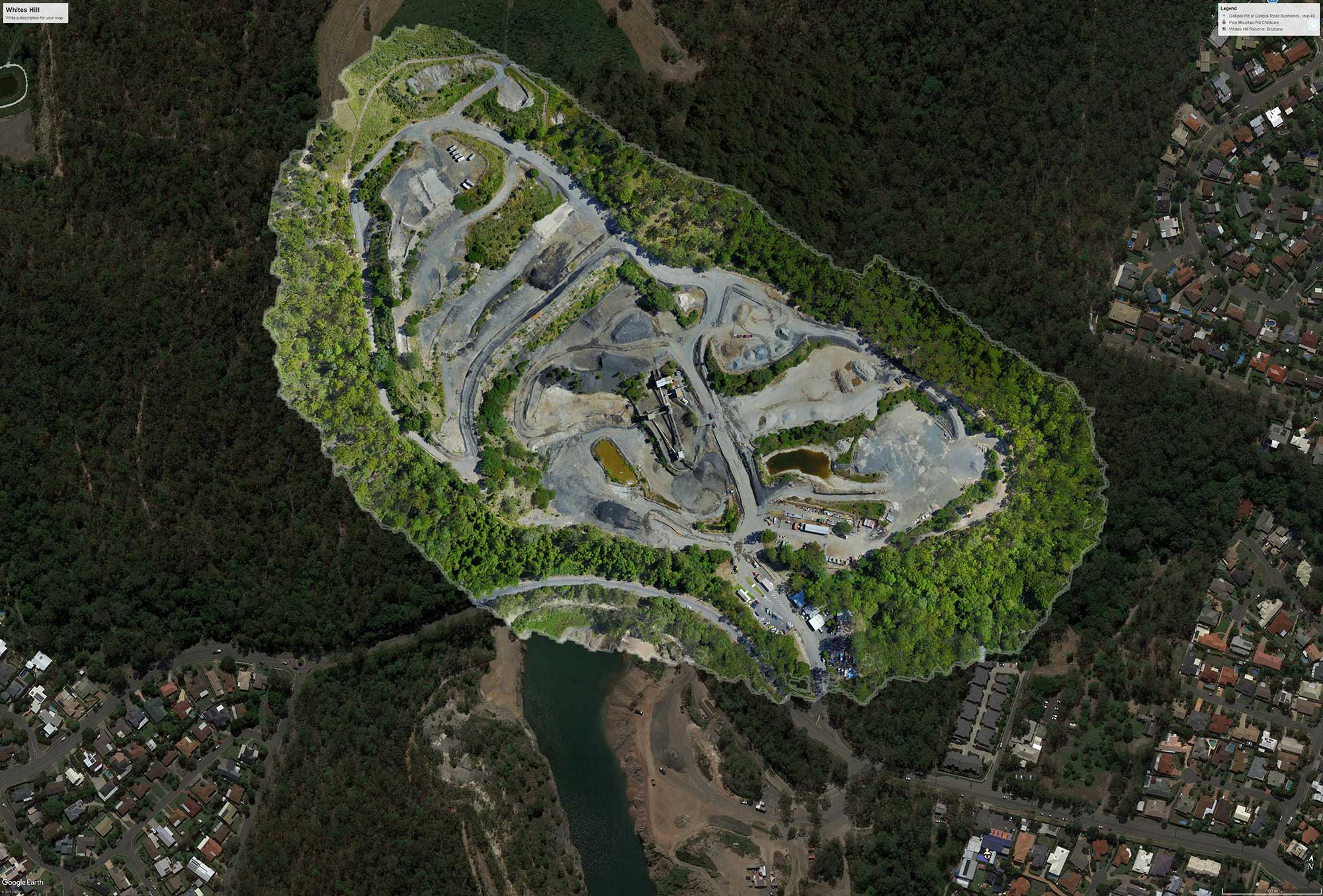
Drone Mapping with the DJI MavicPro
Read more about drone mapping with a DJI MavicPro on our recent Brisbane Quarry drone mapping project.
Contact DroneAce
Are you looking for end-to-end unmanned aerial drone solutions for your project or business needs